9.1 TND Serialization Definition TND序列化定义
9.1.1 TNDS XML usage TNDS XML使用
This specification defines how to transform between a management sub-tree and xml structure. The DTD used for this is the same as defined in [DMTND]. A XML document complying with this specification has a similar but different content than the [DMTND] specification. Therefore a document complying with this specification MUST use a specific MIME-type to indicate it. It is also possible to use the WBXML encoding mechanism defined in [DMTND]. The two MIME-types, one for XML and one for WBXML are specified in Appendix.
这个规范定义了如何在管理子树和xml结构之间转换。用于此的DTD与[DMTND]中定义的相同。符合本规范的XML文档具有与[DMTND]规范类似但不同的内容。因此,符合本规范的文档必须使用特定的MIME类型来表示它。也可以使用[DMTND]中定义的WBXML编码机制。两个MIME类型,一个用于XML,一个用于WBXML,在附录中指定。
9.1.2 General 总体
During runtime the client’s management tree will contain interior nodes and leaf nodes. The client may take a snap-shot on the management tree or a subset of the management tree and convert all information of that part of the management tree into either an xml or a wbxml stream. Some fields are optional and some are mandatory to support. The description for all properties is defined in [DMTND]. Properties which are optional in the management tree may not be stored in the file.
在运行时期间,客户端的管理树将包含内部节点和叶节点。客户端可以在管理树或管理树的子集上进行快照,并将管理树的该部分的所有信息转换为xml或wbxml流。一些字段是可选的,一些是强制支持的。所有属性的描述在[DMTND]中定义。在管理树中可选的属性可能不会存储在于文件中。
The DTD in [DMTND] defines the format of the xml or wbxml file. This specification will not define any transport binding for the xml or wbxml byte stream.
[DMTND]中的DTD定义了xml或wbxml文件的格式。此规范不会为xml或wbxml字节流定义任何传输绑定。
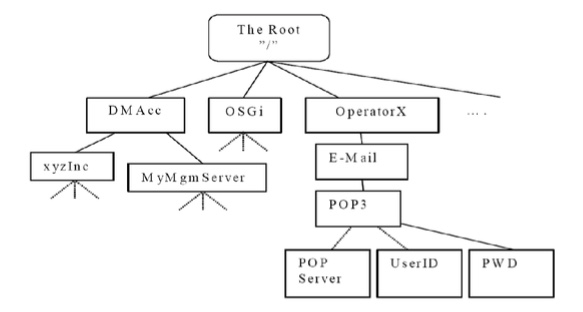
The following figure shows an example of a management tree. With this specification it is possible for the device to translate the E-Mail Management Object to or from an xml or wbxml file.
下图显示了管理树的示例。使用此规范,设备可以将电子邮件管理对象转换为xml或wbxml文件或从这些文件中转换。
9.1.3 DM Commands with TNDS data DM命令与TNDS数据
The format of the TNDS object as byte stream has it own MIME-type. Therefore if the device and server support this MIME- type it is possible to use DM commands and operate on a complete sub tree in one command. The behavior for these commands are described in [DMREPPRO].
作为字节流的TNDS对象的格式具有它自己的MIME类型 因此,如果设备和服务器支持这种MIME类型,则可以使用DM命令并且在一个命令中对完整的子树进行操作。这些命令的行为在[DMREPPRO]中描述。
For example the server will be able to create a large complete structure including data with one single Add command.
例如,服务器将能够使用一个单独的Add命令创建大的包括数据的完整结构。
This is an example for creating a E-Mail object:
这是创建电子邮件对象的示例:
<Add>
<CmdID>4</CmdID>
<Item>
<Target>
<LocURI>/OperatorX</LocURI>
</Target>
<Meta>
<Format xmlns=’syncml:metinf’>xml</Format>
<Type xmlns=’syncml:metinf’>
application/vnd.syncml.dmtnds+xml
</Type>
</Meta>
<Data>
<MgmtTree xmlns=’syncml:dmddf1.2’>
<VerDTD>1.2</VerDTD>
<Node>
<NodeName>E-Mail</NodeName>
<RTProperties >
<Format>
<node/>
</Format>
<Type><DDFName>com.operatorX.dm/1.0/EMail</DDFName></Type>
</RTProperties>
<Node>
<NodeName>POP3</NodeName>
<Node>
<NodeName>POPServer</NodeName>
<RTProperties >
<Format>
<chr/>
</Format>
<Type ><MIME>text/plain</MIME></Type>
</RTProperties >
<Value >mail.Operatorx.com</Value>
</Node>
<Node>
<NodeName>UserID</NodeName>
<RTProperties>
<Format>
<chr/>
</Format>
<Type><MIME>text/plain</MIME></Type>
</RTProperties>
<Value>UserName</Value>
</Node>
<Node>
<NodeName>PWD</NodeName>
<RTProperties>
<Format>
<chr/>
</Format>
<Type><MIME>text/plain</MIME></Type>
</RTProperties>
<Value>4571F7C34A9876B3</Value>
</Node>
</Node>
</Node>
</MgmtTree>
</Data>
</Item>
<Add>